This one came up unexpectedly during a forced migration from MS SQL 2008R2 to MS SQL 2012.
Background
When the Reference Data System is built on real tables (which user can manipulate via in-system mechanisms), performing a specification search in a classifier (nomenclator) and using different views to represent data in one table requires the use of dynamic queries. It is inevitable. But when we try to INSERT INTO #table FROM OPENQUERY(LINKED_SERVER,'SELECT <...>') the MS SQL 2012 might argue that it would like to know what we are about to return. Like, WITH RESULT SETS (blah-blah). And that is confusing, because this query is dynamic and serves for retrieving data from any table the user desires — we never now the column set. Rebuilding the whole system paradigm was out of discussion, so the idea was to create a static table with the same set of columns, and work with it.
The Guessing
It is a CLR function, which returns the guessed schema whenever we supply it with a query.
public class tableDefinitionClass
{
[SqlFunction(DataAccess= DataAccessKind.Read)]
public static SqlString getSchemaByQuery(SqlString query)
{
try
{
string schema="";
string sql=query.ToString();
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection("context connection=true");
conn.Open();
SqlCommand command = null;
SqlDataReader reader = null;
while(sql.IndexOf("'{") > 0)
sql = sql.Substring(0,sql.IndexOf("'{") + 1) + sql.Substring(sql.IndexOf("}'") + 1, sql.Length - sql.IndexOf("}'"));
while(sql.IndexOf("{") > 0)
sql = sql.Substring(0,sql.IndexOf("{"))
+ (sql.Substring(sql.IndexOf("{"),sql.IndexOf("}")-sql.IndexOf("{")).Contains("|") ? " 1=0 " : "''")
+ sql.Substring(sql.IndexOf("}") + 1, sql.Length - sql.IndexOf("}") - 1);
try
{
command = new SqlCommand(String.Format(sql),conn);
reader = command.ExecuteReader();
}
catch
{
conn.Close();
return null;
}
DataTable td = reader.GetSchemaTable();
foreach (DataRow myField in td.Rows)
{
string ColumnName="";
string ColumnSize="";
string NumericPrecision="";
string NumericScale="";
string DataTypeName="";
foreach (DataColumn myProperty in td.Columns)
{
switch (myProperty.ColumnName.ToString())
{
case "ColumnName": {ColumnName = myField[myProperty].ToString();break;}
case "ColumnSize": {ColumnSize = myField[myProperty].ToString();break;}
case "NumericPrecision": {NumericPrecision = myField[myProperty].ToString();break;}
case "NumericScale": {NumericScale = myField[myProperty].ToString();break;}
case "DataTypeName": {DataTypeName = myField[myProperty].ToString();break;}
}
}
schema += ColumnName + " " + DataTypeName;
if( DataTypeName == "binary"
|| DataTypeName == "char"
|| DataTypeName == "nchar"
|| DataTypeName == "nvarchar"
|| DataTypeName == "varchar"
|| DataTypeName == "varbinary"
)
schema += "(" + (ColumnSize=="2147483647"?"max":ColumnSize) + ")";
else if(DataTypeName == "datetime2"
|| DataTypeName == "datetimeoffset"
|| DataTypeName == "time"
)
schema += "(" + NumericScale + ")";
else if(DataTypeName == "decimal"
|| DataTypeName == "numeric"
)
schema += "(" + NumericPrecision + "," + NumericScale + ")";
schema += ",";
}
if(schema.Length > 1)
schema = schema.Substring(0, schema.Length - 1);
return schema;
}
catch
{
return null;
}
}
}
The Query
SELECT SYSDB.dbo._getSchemaByQuery('SELECT * FROM AdventureWorks2008.SalesLT.Customer')
The Result
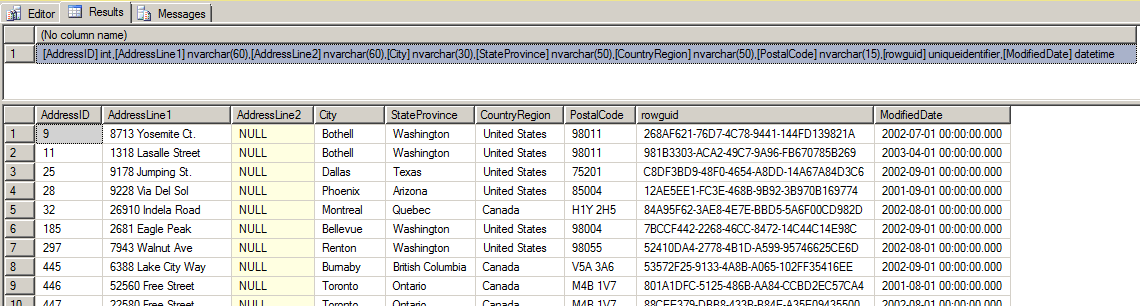
Notes
A question for us: which connection should the CLR function use to run the query? Should we pass some ConnectionString as a parameter?
An answer for us:
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection("context connection=true");No matter what database context we use — it will be lost. So, writing
USE AdventureWorks2008 GO SELECT SYSDB.dbo._guessSchemaByQuery('SELECT * FROM Address')will result in
NULL. If we want this thing to work, we should specify databases explicitly:SELECT SYSDB.dbo._guessSchemaByQuery('SELECT * FROM AdventureWorks2008.SalesLT.Address')The function, which connects to the DB, has to be with
[SqlFunction(DataAccess=DataAccessKind.Read)]. Otherwise, there might be troublees with linking because of security.
Try it
If you want to use this function, download here.