This is the continuation of a post about viewing all table columns.
What For?
Have you ever wanted to just tell MS SQL
Copy the row of
[AdventureWorks2008].[SalesLT].[Product]withProductID=986!
and it would just copy the row? Not that you enumerated all the columns in an INSERT and SELECT clauses. But instead you wrote: copy, please. Wouldn't it be nice? If the table schema changed, you wouldn't need to enumerate another column.
Let me demonstrate.
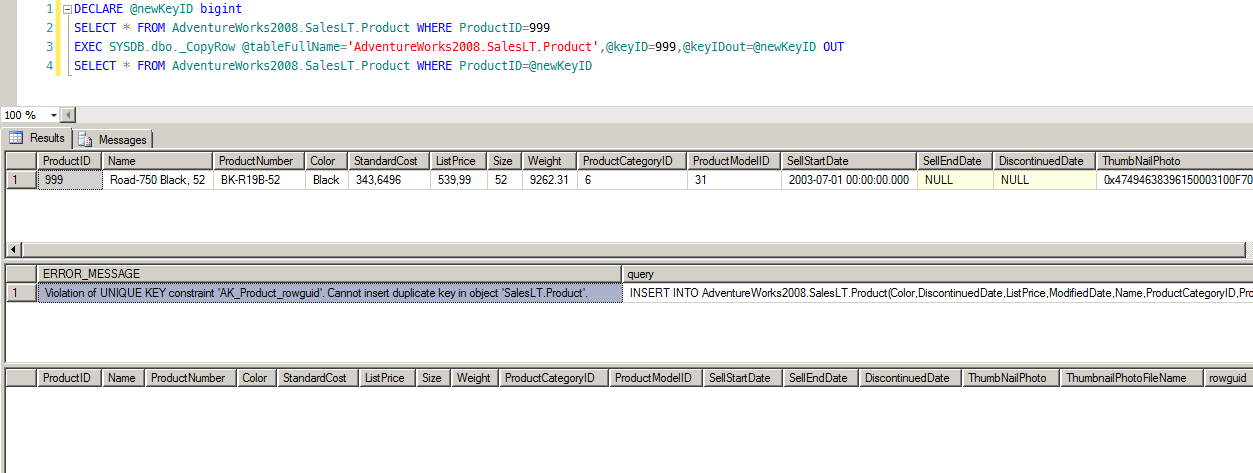
Sorry, but he said that unique index is stopping him from doing that. OK. Let's be gentle this time:
Would you kindly copy the row of
[AdventureWorks2008].[SalesLT].[Product]withProductID=986, but set a new GUID for therowguid, newNameand newProductNumber?
Asking gently:
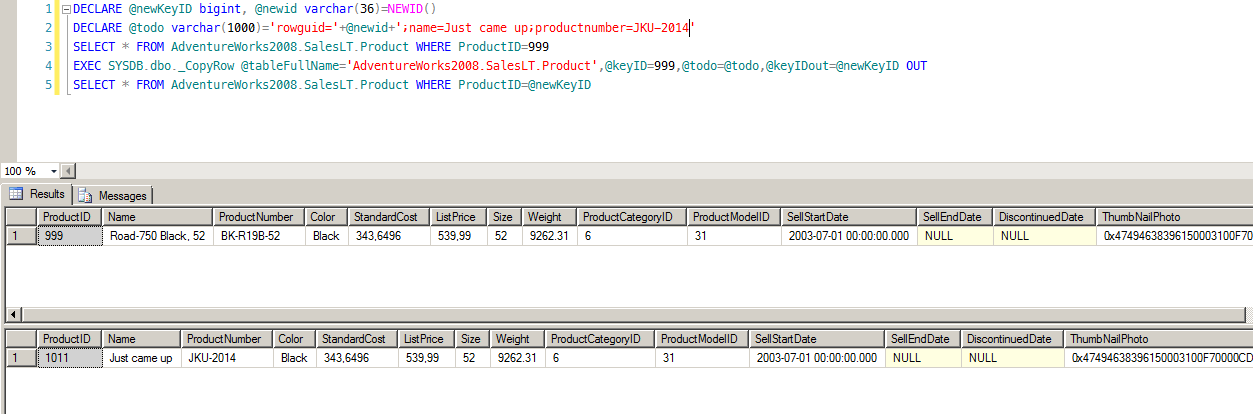
That's it. MSSQL has just copied a row without specifying any INSERT or SELECT columns on our side. Needless to say how helpful that is sometimes.
How It Works
If you can't wait to reproduce, scroll to the bottom of this page for instructions.
We store table schemas in a special table of our 'system' database. When the right time comes, we can get a table's list of columns enumerated in a string, e.g. col1, col2, col3 and create a dynamic query where we would concatenate things like INSERT INTO and OUR TABLE and (col1, col2, col3) and SELECT and col1, col2, col3 and FROM and OUR_TABLE and WHERE $IDENTITY= and OUR_PRODUCT_ID_VALUE. Moreover, if we need to put some changes to the values, we simply replace some of the colN names with explicit values, like SELECT col1, 'new value', col3 FROM OUR_TABLE.
Once we have the query, we run it, and the magic happens.
If we ever add new columns to our table, we ask a special procedure to 'refresh' all schemas, and the column gets enumerated along with others, so we don't need to keep track of any copying routines in our system.
Here Comes the Inside
If you're interested in the mechanism behind such functionality — be my guest.
Prerequisites
This script implies working with regular expressions, concatenation aggregate and arrays. The CLR DLL can be found here.
Storing Table Schemas in One Place
If you read the previous post, you'll see that we simple store all database.table schemas in a static table instead of viewing a single table's set of columns.
if OBJECT_ID('SYSDB.._table_schemas') IS NULL
CREATE TABLE SYSDB.._table_schemas(
[db] [varchar](32) NOT NULL,
[object_id] [int] NOT NULL,
[name] [sysname] NULL,
[type] [sysname] NOT NULL,
[column_id] [int] NOT NULL,
[is_nullable] [bit] NULL,
[is_identity] [bit] NOT NULL,
[length] [varchar](10) NULL,
[precision] [varchar](10) NULL,
[scale] [varchar](10) NULL,
[StrLen] [smallint] NOT NULL,
[LITERAL_PREFIX] [varchar](32) NULL,
[LITERAL_SUFFIX] [varchar](32) NULL,
[primary_key] [varchar](1) NULL
)
if (ISNULL(@dbname,'')='') set @objname=NULL
if ISNULL(@objname,'')<>'' set @obj_id=OBJECT_ID(@objname)
DECLARE @tmp_db TABLE (num int identity, dbname varchar(64))
INSERT INTO @tmp_db(dbname) SELECT [name] FROM master..[sysdatabases] WHERE[name]=ISNULL(@dbname,[name])
if (ISNULL(@dbname,'')='') truncate table SYSDB.._table_schemas
else delete from SYSDB.._table_schemas where db=@dbname and object_id=ISNULL(@obj_id,object_id)
select @i=0, @cnt=isnull((select MAX(num) from @tmp_db),0),@dbname=null
while @i<@cnt begin set @i=@i+1 select @dbname=dbname from @tmp_db where num=@i
set @sql="INSERT INTO SYSDB.._table_schemas SELECT '" +@dbname+"' db, C.object_id, C.name, Tp.name AS type, C.column_id, C.is_nullable, C.is_identity,
(CASE when ST.CREATE_PARAMS is null then '' WHEN CHARINDEX(',',ST.CREATE_PARAMS)>0 then CAST(Tp.precision AS varchar(10)) ELSE CAST(C.max_length AS varchar(10)) END) AS length,
(CASE WHEN CHARINDEX(',',ST.CREATE_PARAMS)>0 then CAST(C.scale AS varchar(10)) ELSE '' END) AS scale,
(CASE WHEN CHARINDEX(',',ST.CREATE_PARAMS)>0 then CAST(C.precision AS varchar(10)) ELSE '' END) AS precision,
(CASE WHEN C.precision > 0 THEN C.precision WHEN C.precision = 0 AND C.max_length > 0 THEN C.max_length ELSE Tp.max_length END) AS StrLen,
ST.LITERAL_PREFIX COLLATE Latin1_General_CI_AS AS LITERAL_PREFIX, ST.LITERAL_SUFFIX COLLATE Latin1_General_CI_AS AS LITERAL_SUFFIX,
(CASE WHEN t2.is_primary_key=1 THEN 'Y' END) AS primary_key
FROM "+@dbname+".sys.columns AS C JOIN "+@dbname+".sys.types AS Tp ON(C.system_type_id = Tp.system_type_id)
JOIN SYSDB.._datatype_info AS ST ON(Tp.name COLLATE Cyrillic_General_CI_AS = ST.TYPE_NAME)
left join "+@dbname+".sys.index_columns t1 on(t1.column_id = C.column_id and t1.object_id = C.object_id)
left JOIN "+@dbname+".sys.indexes t2 on(t1.object_id = t2.object_id AND t1.index_id = t2.index_id)"
+(case when ISNULL(@obj_id,0)>0 then " WHERE C.object_id="+CAST(@obj_id as varchar) else "" end)
exec(@sql)
end
That should store the schemas.
Copying a Row
This is the procedure that does the whole thing:
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[_CopyRow]
@tableFullName varchar(1000) /**@param Full table name (AdventureWorks2008.SalesLT.Product)*/
,@keyID bigint /**@param Source row ID (identity value)*/
,@keyIDout bigint=null out /**@param Returned value of inserted identity*/
,@todo varchar(max)=null /**@param String of values to change (col1=2;col2=;col3=newval)*/
AS
BEGIN
set nocount on;
DECLARE @dbname varchar(30)
DECLARE @query nvarchar(max)
DECLARE @columns varchar(max)
DECLARE @key_column varchar(100)
DECLARE @is_identity int
DECLARE @tmp varchar(100)
DECLARE @errDesc varchar(max)
SET @dbname = SYSDB.dbo.arrayAt(@tableFullName,0,'.')
IF NOT EXISTS(select 1 from sys.databases AS db WHERE db.name=isnull(@dbname,''))BEGIN
SELECT 'Database not found'
RETURN END
/*********** full description of the table columns **************************************/
CREATE TABLE #tmp_bfColumn([db] [varchar](32) NOT NULL,[object_id] [int] NOT NULL,[name] [sysname] NULL,[type] [sysname] NOT NULL,
[column_id] [int] NOT NULL,[is_nullable] [bit] NULL,[is_identity] [bit] NOT NULL,[length] [varchar](10) NULL,[precision] [varchar](10) NULL,
[StrLen] [smallint] NOT NULL,[LITERAL_PREFIX] [varchar](32) NULL,[LITERAL_SUFFIX] [varchar](32) NULL,[primary_key] [varchar](1) NULL)
INSERT INTO #tmp_bfColumn([db],[object_id],[name],[type],[column_id],[is_nullable],[is_identity],[length],[precision],[StrLen],[LITERAL_PREFIX],[LITERAL_SUFFIX],[primary_key])
SELECT [db],[object_id],[name],[type],[column_id],[is_nullable],[is_identity],[length],[precision],[StrLen],[LITERAL_PREFIX],[LITERAL_SUFFIX],[primary_key]
FROM SYSDB.._table_schemas
WHERE [OBJECT_ID]=OBJECT_ID(@tableFullName) AND db=@dbname
SELECT @columns = SYSDB.dbo.list(distinct v.name,',') FROM #tmp_bfColumn as v WHERE [name] not in('InsTime','UpdTime','other unwanted columns') and v.is_identity<>1 and v.type<>'sysname'
SELECT @key_column = v.name FROM #tmp_bfColumn as v WHERE v.primary_key='Y' OR v.is_identity=1
BEGIN TRY
BEGIN TRAN linecopy
IF LEN(@columns)=0 OR ISNULL(@key_column,'')='' BEGIN
ROLLBACK TRAN
SELECT 'The table does not exist or it does not have identity/primary key'
RETURN END
/*********** column names and suffixes/prefixes **************************************/
CREATE TABLE #tmp_col (_name varchar(max), LITERAL_PREFIX varchar(10), LITERAL_SUFFIX varchar(10))
INSERT INTO #tmp_col (_name, LITERAL_PREFIX, LITERAL_SUFFIX) SELECT v.name as _name, d.LITERAL_PREFIX , d.LITERAL_SUFFIX
FROM #tmp_bfColumn as v JOIN SYSDB.._datatype_info AS d ON (v.type=d.TYPE_NAME)
/*********** split @todo from 'a=1;b=text;c=3' into table (col,colvalue) *************/
CREATE TABLE #new_values(value varchar(4000), col varchar(100), colval varchar(4000))
INSERT INTO #new_values(value) SELECT Match FROM SYSDB.dbo.RegExSplit(@todo,';',0)
IF @@TRANCOUNT=0 RETURN
/*********** split pairs 'a=1' into two columns: name and value **********************/
UPDATE #new_values SET col=left(value,CHARINDEX('=',value)-1), colval=STUFF(value,1,CHARINDEX('=',value),'')
UPDATE #new_values SET colval = (case WHEN colval='NULL' THEN 'NULL' ELSE ISNULL(#tmp_col.LITERAL_PREFIX,'')+colval+ ISNULL(#tmp_col.LITERAL_SUFFIX,'') END)
FROM #tmp_col WHERE #tmp_col._name=#new_values.col
/*********** all columns with new values *********************************************/
CREATE TABLE #t_all(value varchar(4000), col varchar(100), colval varchar(4000))
INSERT INTO #t_all(value) SELECT Match FROM SYSDB.dbo.RegExSplit(@columns,',',0)
IF @@TRANCOUNT=0 RETURN
update #t_all set colval=(select max(tx.colval) from #new_values tx where tx.col=#t_all.value)
update #t_all set colval=CAST(@keyIDout AS varchar(max)) where value=@key_column
/****** assemble the query, replacing column names with new values if necessary ******/
SELECT @query = 'INSERT INTO '+@tableFullName+'('+APSYS.dbo.list(t.value,',')+')'
+' SELECT '+APSYS.dbo.list(case when t.colval is null then t.value else t.colval+' '+t.value end,',')
+' FROM '+ @tableFullName + ' WHERE ' + @key_column + '=' + CAST(@keyID as varchar(10))
FROM #t_all as t
EXEC(@query) IF @@ROWCOUNT>0 SET @keyIDout=@@IDENTITY ELSE RAISERROR('Record not created', 16, 1)
COMMIT TRAN linecopy
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
IF @@TRANCOUNT=0 RETURN
ROLLBACK TRAN
SELECT ERROR_MESSAGE() as ERROR_MESSAGE,@query as query
SET @keyIDout = -1
END CATCH
set nocount off;
END
GO
We create a temporary table and put there information about our table (the one which we chose as a subject of copying a row). We also find an identity column. Then we prepare columns with LITERAL_PREFIX and LITERAL_SUFFIX in case we put explicit values. For example, INSERT INTO table(int_col, varchar_col, varbinary_col) SELECT 1, 'text', 0xCA010. The '' and 0x are exactly those. We split the @todo array (e.g., a=10;b=new text;c=value) into a table to create the key => value tuples. In the final column table we place values if they were given.
The final step is to assemble a query using the SYSDB.dbo.list concatenation aggregate.
SELECT @query = 'INSERT INTO '+@tableFullName+'('+SYSDB.dbo.list(t.value,',')+')'
+' SELECT '+SYSDB.dbo.list(case when t.colval is null then t.value else t.colval+' '+t.value end,',')
+' FROM '+ @tableFullName + ' WHERE ' + @key_column + '=' + CAST(@keyID as varchar(10))
FROM #t_all as t
Instructions
If you wish to repeat the topic functionality, you need four things:
- Create a 'system' database. I called it
SYSDB; - Import CLR functions from here;
- Run these scripts:
- Save information about data types;
- Create and run a procedure to refresh schemas.
- Create a procedure that copies a row.
- Enjoy.